CONTACT US BY PHONE
Crosslinking
Corneal crosslinking is a modern medical treatment specifically designed to stop or significantly slow the progression of keratoconus. However, this method is also used to treat corneal ectasia (thinning and bulging of the cornea) after laser surgery on the cornea.
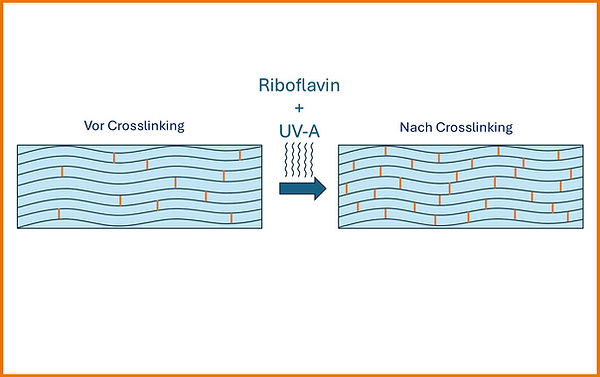
In crosslinking, the cornea is stabilized through the formation of new cross-links between collagen fibers. This makes the cornea more rigid and less deformable.
The goal of the treatment is to halt the progression of keratoconus, meaning to stop the conical deformation of the cornea. This helps to achieve stable visual acuity and to delay or avoid the need for a corneal transplant.
For the procedure, the affected eye is numbed with anesthetic eye drops (topical anesthesia). A key part of the treatment involves saturating the cornea with vitamin B2 (riboflavin) drops for 30 minutes. Riboflavin is photosensitive and prepares the cornea for the next step. The cornea is then irradiated for 10 to 30 minutes with UV-A light (365 nm). In combination with riboflavin, reactive oxygen molecules are formed, creating new cross-links between the collagen fibers as illustrated in the figure. This makes the cornea firmer and more stable, in a way similar to tissue reinforced with additional sutures.
After the procedure, it is generally recommended to wear a protective contact lens for several days to reduce foreign body sensation. Postoperative treatment with antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops is also provided.

